|
|
|
|
 |
|
| A study of MADAGASCAR AMETHYST |
|
|
| ( SiO2 ) Faceted Amethyst click here ! |
|
|
| (Variety of Quartz) |
 |
| · Crystallographic properties: |
| Trigonal System (Subdivision of the hexagonal system) |
|
| Crystal structure of amethyst : |
| Quartz forms hexagonal prisms at the blunted ends and the head |
| finishing in hexagonal pyramids. |
|
| · Physical properties |
| Hardness 7 |
| Density 2.65 - 2.66 |
| Refractive Index: 1.54 -1.55 + 0.009 positive uniaxial |
| Glare: vitreous |
|
| · Chemical Composition: |
|
| Silicium Dioxide ( SiO2 ) |
|
| The colouring of amethysts is due to the presence of colour centers which come from substitution of ions of |
| silicon by iron ions in the crystal lattice of quartz. |
| For example, the amethyst crystallizes at lower temperatures than smoky quartz.In Madagascar, we find it either in |
| crypts of pegmatites, or in quartzite veins in connection with those. |
| The geodes of the siliceous nodules of basalts contain some too. |
| The first have an hexagonal network, although their pattern of crystallization is only of ternary order. The seconds |
| have a ternary network. The elementary mesh is a rhomboedron, i.e. a parallelepiped consisted six equal |
| rhombuses. |
|
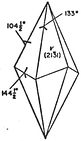
| A ternary axis A3 joint the tops of the regular trihedrons, three normal binary axes A2 with the ternary axis joining |
| the meddle of opposite horizontal corners. |
|
|
 |
 |
| Here elements of symmetry of the Trigonal system with |
| the oblique shape, the tetragonal scalenoedron. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
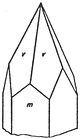
| It is interesting to see what becomes this tetragonal scalenoedron in others classes where the disappearance of |
| the symmetry planes makes decrease of half the number of the faces. We obtain a trapezohedron (One notices that |
| these two trapezohedrons are not superposable. It is said that they are two enantiomorphism shapes. They are |
| symmetrical compared to a symmetry plane.) |
|
|
One speaks about right trapezohedron and left trapezohedron (just as we have a right hand and a left hand,
|
|
nonsuperposable thus enantiomorphism).
|
|
| Certain minerals present sometimes left forms sometimes right forms. The most known example is that of quartz. |
| The distinction between left quartz and right quartz has a certain importance in the electronics industry where one |
| uses the piezo-electric properties of this mineral. |
|
|
|
|
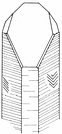
| The negative crystals of hexagonal shape can contain liquids like water, gas, as well as rutile needles, tiny hematite |
| discs, goetite, fushsite or mica. |
|
|
|
|
 |
Inclusions of H2O and CO2 in an amethyst from Madagascar. Habitus type of flattened Dauphiné. |
 |
|
|
 |
This marvellous Bi-terminated amethyst of 128 grams also contains water drops in its center. Habitus type of rhomboedron.
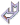 Enlarge Enlarge
|
|
|
The amethyst scepters are also typical in Madagascar. |
|
|
|
|
 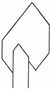 |
 |
|
|
|
Here, a scepter in the blackberry shape. |
 |
 |
|
 |
There, the stem of the scepter developed by crystallizing around it a quantity of small points in hedgehog. Length:40 mm.
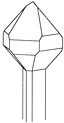
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Amethyst in castle on its quartz gangue. 986 grams.
Enlarge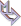
|
 |
|
| The fact that sometimes a thin surface layer of violet color be only presents in the stone or that this color is not |
| homogeneous, makes often a difficult cutting. The art of lapidary is to place the color correctly in order to make |
| homogeneous the tone of cut stones. The distribution of the color in a cut stone is observed simply by |
| immersing it in water contained in a transparent container and colourless. The color of amethyst varies from purple |
| reddish to purple bluish while passing by straightforwardly crimsons tone. Thus of very variable intensity, the color |
| is often laid out in stripes parallel to the final faces of the crystal. |
|
|
 |
 Enlarge Enlarge
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
 |
Your guide to GGGems |
 |
©  All of the pictures on this website have been shot by gggems.com All of the pictures on this website have been shot by gggems.com |
Alain Darbellay |
| Text written by Alain Darbellay. |
|
|